Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (16): 2594-2600.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.16.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
A three-dimensional nanofiber scaffold provides an appropriate microenvironment for stem cell regulation
Bai Shu-meng, Liu Xi
- National Engineering Laboratory for Modern Silk, College of Textile and Clothing Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2014-02-03Online:2014-04-16Published:2014-04-16 -
Contact:Liu Xi, M.D., Associate professor, National Engineering Laboratory for Modern Silk, College of Textile and Clothing Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Bai Shu-meng, M.D., National Engineering Laboratory for Modern Silk, College of Textile and Clothing Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, No. BK20130309; the Natural Science Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Jiangsu Province, No. 13KJB430019; China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, No. 2013M541724
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Bai Shu-meng, Liu Xi. A three-dimensional nanofiber scaffold provides an appropriate microenvironment for stem cell regulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2594-2600.
share this article
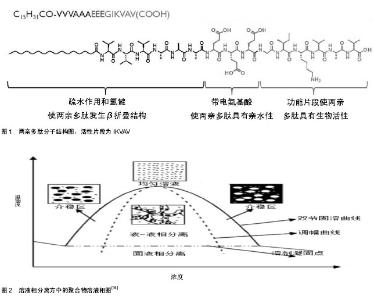
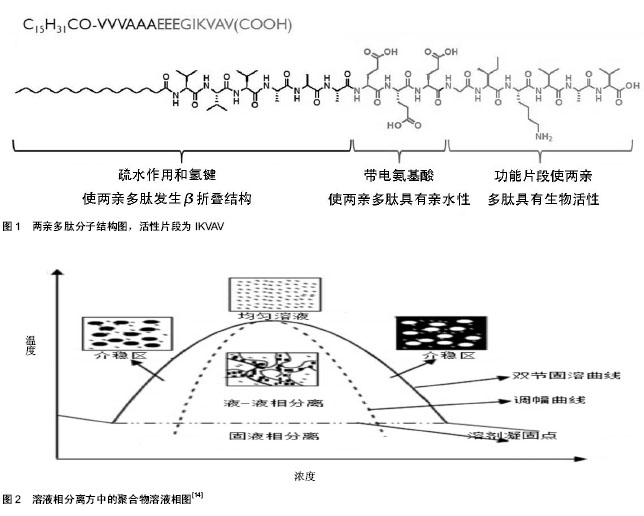
2.1 纳米纤维三维支架材料的制备 体外模拟干细胞微环境的第一步是明确天然微环境的物理结构。虽然可能不同的细胞微环境种类各有特点,然而他们的共同特点是纳米纤维形貌。纳米制造与合成技术包括分子自组装技术、溶液相分离和静电纺丝技术技术等,为体外构建干细胞三维微环境提供了可能性。 自组装是结构单元在基于非共价键的相互作用下自发的组织或聚集成为一个稳定的、具有一定规则几何外观有序结构的过程[6-7]。自组装普遍存在于生命体系中,是生命本质的内容之一,比如DNA分子的螺旋结构便是自组装的结果。基于自组装技术,人们制备出了许多纳米物质,包括零维物质、球形胶束、柱形胶束、二维膜片、三维网络等[8]。 分子形状和分子间相互作用力可以影响自组装过程,导致拓扑结构的多样性[9]。1992年张曙光博士在酵母蛋白中发现了离子短肽EAK16,并在此基础上自组装出具有β折叠结构的自组装多肽RADA16[10],引发了分子自组装技术在生物材料制备中应用的风潮。RADA多肽主要由极性与非极性氨基酸交替排列构成,非极性氨基酸形成疏水端,极性氨基酸形成亲水端。在水溶液中,疏水端聚集在内侧,极性氨基酸聚集在外侧;外侧的极性氨基酸由正负电的R和D交替排列,亲水端氨基酸通过离子间相互作用交替排列使多肽分子自组装并延长形成稳定的纳米纤维。在pH值改变为中性时,RADA多肽分子便形成含水量达99%的水凝胶。 两亲多肽(C15H31COCCCCGGGXXXX)是另一种常见自组装单元(图1),主要由4部分组成:疏水烷基链,保证多肽分子具有两亲性;β折叠部分;带电多肽部分,使多肽分子具有亲水性;活性片段区域(XXXX,可变化),一般是活性功能短肽片断,用来调节细胞的生长和分化。它的的自组装可以在生理pH和离子强度下发生,因此这种两亲多肽纳米纤维支架材料可以包裹细胞进行三维培养,具有广阔体内应用前景[11]。自组装多肽水凝胶除了在物理结构上高度模拟细胞外基质,其最大的优点之一是能够在合成过程中接枝功能短肽片段,赋予材料特定的生物功能,可以为细胞提供特定的生物活性信号。例如,在RADA16上接枝RGD短肽可以显著提高细胞的黏附和增殖;接枝血管生长因子模拟短肽片段可以促进内皮细胞增殖并形成管腔状结构;在两亲多肽分子上接枝IKVAV可以促进神经干细胞向神经元方向分化。然而自组装纳米纤维缺乏长程有序性,故而难以实现定向排列。Zhang等[12]通过热处理实现了两亲自组装多肽纳米纤维的长程定向排列,进一步拓宽了自组装多肽材料的应用。 在溶液相分离中,聚合物溶液可以在加热的情况下发生相分离。在特定的条件下,相分离的聚合物具有纳米纤维结构[13]。溶液相分离法制备纳米纤维支架材料一般需要凝胶相分离、溶剂萃取、冷冻和冻干(图2)。通过这种方法制备的支架材料纤维直径一般在几十至几百个纳米[14]。采用这种方法可以制备出具有微米孔径和纳米纤维的明胶支架材料以模拟细胞外基质中Ⅰ型胶原的纳米拓扑结构和化学成分[15]。溶液相分离方法操作容易,设备简单,易批量生产,并且控制孔隙率和孔径大小相对容易,但这种方法只能制备出各向同性的支架材料。 静电纺丝是纳米纤维支架材料制备的普遍方法,具有操作简单、可控性强、成本低廉、可纺物质种类多等优势[16]。电纺丝装置一般包括喷头、注射泵和接收器,通过在喷头和接收器之间加载电压,挤出的溶液表面富集电荷,随着溶液表面静电斥力的不断增强,针头处的溶液呈现圆锥状(即泰勒锥);当静电斥力大于溶液的表面张力时,纤维状的溶液就会从泰勒锥中喷出,最后由收集装置收集便得到支架材料。在纺丝过程中,黏性射流经过加速和拉伸后形成小尺寸的纤维,其直径一般在几十个纳米至几个微米之间。电纺丝操作虽然简单,但其过程十分复杂。溶液的黏度、电压、温度、湿度、接收器与喷头的距离、溶液加载流速等均会影响纤维支架材料的尺寸和形貌。需要系统优化这些参数,才能够获得理想的纳米纤维支架材料。 通常情况下,直接纺丝得到的是各向同性纳米纤维,通过改变接收器的形式可以得到定向排列的纳米纤维[17],这也是静电纺丝技术由于其他两种技术的一方面。静电纺丝现在可以应用于聚合物共混物、核壳结构纤维、以及天然高分子。目前可纺的天然高分子包括胶 原[18]、壳聚糖[19]、明胶[20]、透明质酸[21]、粘连蛋白等[22]。作为组织工程支架,静电纺丝材料被广泛用于各种干细胞的培养。"

2.2 纳米纤维三维支架材料调控干细胞命运 干细胞具有自我更新和向特定组织细胞分化的潜力,是组织工程和再生医学中具有广阔应用前景的细胞。当前干细胞在组织工程中的主要研究方向是:通过生物材料模拟体内干细胞微环境,促进干细胞分化,在保存干细胞活性的基础上提升其自我更新能力。干细胞对其周围环境敏感,它会对周围环境(从微米级到分子级)做出响应行为[24]。纳米纤维支架材料首先可以在结构上模拟干细胞微环境,复合生物化学信号和活性小分子以更加全面地实现体内微环境重构,调控干细胞的增殖和分化。 2.2.1 调控干细胞体外增殖 充足的干细胞数量是组织工程干细胞治疗成功的前提条件。然而从机体组织分离提取的干细胞数量有限,所以需要采取适当的体外培养方法来进行干细胞扩增。体外扩增的干细胞质量(干细胞表型和再生潜能)和纯度(杜绝其他细胞类型的污染)也十分重要。因此,需要一个既可以提高干细胞数量又可以保持干细胞活性的体外培养方法。 造血干细胞:造血干细胞存在于体内骨髓微环境中,它可以在体内保持自我更新和分化的活性,在体外培养时很容易丧失自我更新能力。造血干细胞在体内能够保持活性的原因在于骨髓微环境的生物化学性质和拓扑结构[25]。因此成功的体外造血干细胞扩增体系应能够在最大程度上模拟骨髓干细胞的微环境。目前造血干细胞体外扩增的培养方法大致可以分为两大类:生物学方法和生物材料方法。 生物学方法采用基质单层膜为造血干细胞提供生物学信号[26]。培养体系上黏附一层含有成纤维细胞、巨噬细胞、脂肪细胞、内皮细胞和网状细胞的基质细胞层,在该细胞层上进行造血干细胞培养。这种培养方法可使造血干细胞长时间保持自我更新能力,但同时有着无法避免的缺点:基质细胞层生命周期具有时限性,一般为6-8周。更重要的是,这种培养方法给临床应用带来了诸多不便;基质细胞层的采集和培养耗时很长,拖长了治疗周期和增加了治疗费用,并且影响到了自体造血干细胞纯度;很难从患者身体提取健康的基质细胞;基质单层膜的成分尚不能完全确定,导致该方法可重复性低,造血干细胞的扩增时 间无法预期。 生物材料方法通过模拟骨髓的三维微环境来为造血干细胞提供类似体内的生长微环境。诸多研究表明,三维培养有利于造血干细胞体外增殖和分化。Bagley等[27]发现三维钽多孔支架材料可维持造血干细胞活性达6周,并且在无血清和细胞因子的情况下实现6.7倍增殖。与二维培养相比,将造血干细胞培养在无纺PET支架材料上,在7-9周后能够获得较高比例的CD34+细胞[28]。 胚胎干细胞:胚胎干细胞在体外培养必须通过滋养层细胞维持其活性。Eur-E-Kamal等[29]采用静电纺丝聚酰胺纳米纤维支架材料(Ultra-Web)研究三维纳米纤维支架材料对胚胎干细胞增殖和自我更新的影响。观察发现,培养在Ultra-Web三维支架材料上的胚胎干细胞处于未分化状态,并且集落尺寸比培养在二维玻璃片上的大很多。机制研究表明,纳米纤维支架材料有助于激活胚胎干细胞Rac和PI3K/AKT信号通路,上调了Nanog和c-Fos的表达,从而刺激干细胞增殖。 间充质干细胞:静电纺丝胶原纳米纤维支架材料可用于体外间充质干细胞的扩增培养。Shih等[30]研究了间充质干细胞在该支架上的体外扩增。与培养板上培养的间充质干细胞相比,胶原纳米纤维支架材料上的干细胞表达出较多的黏着斑。表明间充质干细胞与细胞骨架相关联的信号通路受到胶原纳米纤维支架材料的刺激。与培养板相比,胶原纳米纤维支架材料在调控干细胞增殖方面具有显著优势。Hosseinkhani等[31]研究了间充质干细胞在自组装多肽纳米纤维水凝胶中的增殖情况。通过细胞黏附片断RGD模拟干细胞微环境中活性因子,并将其接枝在自组装多肽纳米纤维支架材料上获得了复合RGD片断的支架材料,该支架材料能够显著提升干细胞的黏附和增殖。 神经干细胞:神经干细胞的体外扩增一般是通过与基质细胞共培养或者在生长因子的刺激下球状悬浮培养[32-33]。然而这两种培养方法都有局限性:第一种方法在临床应用时会有异种细胞污染的可能,而第二种方法效率较低。Christopherson等[34]用层粘连蛋白对静电纺丝聚醚砜支架材料表面改性,并在此基础上研究支架纤维直径(283,749,1 452 nm)对神经干细胞增殖的影响:随着纤维直径的减小,神经干细胞增殖数量上升。通过扫描电镜细胞形貌观察发现:在283 nm直径的纤维支架上,神经干细胞以集落形式存在,细胞与细胞之间联系紧密;而在培养板上的神经干细胞呈铺展状态,细胞之间的联系较弱。结果说明纳米纤维结合层粘连蛋白可以调节神经干细胞之间,以及神经干细胞与基质之间的相互作用,从而影响神经干细胞的增殖和迁移。Nisbet等[35]将大鼠神经干细胞移植在直径750 nm氨基化静电纺丝聚己内酯支架上,发现其能够提高神经干细胞的黏附和增殖。 2.2.2 调控干细胞体外分化 在干细胞治疗中,干细胞的分化潜力与干细胞的数量一样重要。干细胞分化一方面可以由小分子物质(生长因子)来调控,另一方面也受到微环境中物理和化学信号的影响。可以将这些因素复合到纳米纤维支架材料中,借助纳米纤维支架材料最大程度上复制体内干细胞微环境的各种信号,模拟干细胞微环境,制备出更适于组织工程和再生医学的生物材料。纳米纤维支架材料调控干细胞分化主要包括以下几个方面: 调控间充质干细胞向骨和软骨方向分化:间充质干细胞有着取材容易、培养和扩增简单,并且具有向骨、软骨等多方向分化潜力的优势,一直是干细胞移植治疗的首选细胞[36]。骨组织修复的支架材料通过复合与骨细胞微环境成分近似或相同的无机物来促进天然骨组织和支架材料之间的结合,诱导新骨再生[37]。磷酸钙和羟基磷灰石具有很好的生物相容性和生物活性[38],但是存在着易碎的缺点,应用范围受到限制。将无机物纳米颗粒混合在溶液 中[39],然后通过静电纺丝制备出的纳米纤维支架材料[40],可以促进间充质干细胞向成骨方向分化。Lee等[41]将羟基磷灰石混合在聚乳酸/羟基乙酸共聚物纳米纤维支架材料中,提高了间充质干细胞碱性磷酸酶活性和成骨基因的表达。在软骨组织修复中,多孔的纳米纤维支架材料为软骨内膜细胞之间以及细胞与基质之间的相互作用提供了一个适宜的微环境。静电纺丝聚己内酯纳米纤维支架材料上的间充质干细胞,在转化生长因子β1诱导下分化成软骨的效果显著优于传统的高浓度团状培养方法[42]。 调控干细胞向神经方向分化:神经组织缺乏自我再生能力,因此神经修复一直是研究的热点。干细胞移植治疗为中枢神经和外周神经修复带来了希望。纳米纤维支架材料的拓扑结构可以有效刺激干细胞向神经方向分化,调控干细胞形貌、黏附及神经突起的延伸[43]。相比于各向同性的支架材料,取向的纳米纤维支架可以更加有效地促使干细胞向神经方向分化[44-46]。Chew等[47]通过静电纺丝制备了定向纳米纤维支架,并研究了其对于许旺细胞成熟的影响。定向纳米纤维支架可有效促进轴突再生和神经功能的修复[48]。神经干细胞培养在多肽纳米纤维支架材料上,50%向神经元方向分化;而培养在二维培养皿上的神经干细胞只有10%向神经元方向分化[49]。 调控干细胞向肌肉方向分化:肌肉组织具有高度有序的排列结构,因而模拟其微环境基底膜结构的定向纳米纤维支架材料是肌肉组织工程的主要材料。定向羟丁基壳聚糖纳米纤维支架材料比无序支架材料更加能够促进干细胞肌源性基因(结蛋白、肌细胞生成素等)表达的上升,诱导取向排列肌小管的形成[50]。Choi等[51]发现与无序聚己内酯支架相比,取向聚己内酯支架上肌小管的长度翻倍。 2.2.3 调控移植干细胞体内命运 动物实验证明简单的静脉注射或者向受损组织注射干细胞可以实现机体功能的修复[52-54],然而只有骨髓移植是目前临床干细胞治疗中惟一成功的案例。干细胞移植治疗失败的主要原因在于不能有效控制移植干细胞的命运[55]:受损组织的微环境不能提供适当的信号使其保持活性,因而干细胞大量凋亡。本着改善干细胞移植治疗效果的目的,为干细胞移植提供微环境的支架材料应运而生。这些支架材料承担了细胞外基质的角色,一方面起到支撑作用,另一方面调控干细胞向被修复组织方向分化。Li等[56]报道了静电纺丝纳米纤维聚己内酯支架材料在猪关节软骨修复中的应用。Hashi等[57]用管状左旋聚乳酸 纳米纤维支架材料改善血管组织工程的修复效果。多肽材料的可注射性使干细胞移植的操作简单易行。Davis等[58]将RADA-Ⅱ自组装多肽水凝胶注射到成年小鼠左心室,为体内内皮细胞和平滑肌细胞提供了一个良好的微环境。"

| [1] Engler AJ,Sen S,Sweeney HL,et al.Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification.Cell.2006;126(4):677-689.
[2] Smith LA,Liu X,Hu J,et al.Enhancing osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells by nanofibers. Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(7):1855-1864.
[3] Martino S,D'Angelo F,Armentano I,et al.Hydrogenated amorphous carbon nanopatterned film designs drive human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell cytoskeleton architecture.Tissue Engineering Part A.2009;15(10): 3139-3149.
[4] Kopp HG,Avecilla ST,Hooper AT,et al.The bone marrow vascular niche: home of HSC differentiation and mobilization.Physiology (Bethesda).2005;20:349-356.
[5] Branden C,Tooze J.Introduction to protein structure. Ed. Garland New York, 1991.
[6] Whitesides GM,Grzybowski B.Self-assembly at all scales. Science.2002; 295(5564):2418-2421.
[7] Stupp SI.Introduction:functional nanostructures.Chem Rev. 2005; 105(4):1023-1024.
[8] Lehn JM.Supramolecular chemistry:from molecular information towards self-organization and complex matter. Rep Prog Phys.2004;67:249.
[9] Israelachvili JN.Intermolecular and surface forces. Ed. Academic press,2011.
[10] Zhang S,Holmes T,Lockshin C,et al.Spontaneous assembly of a self-complementary oligopeptide to form a stable macroscopic membrane.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.1993;90(8): 3334-3338.
[11] Silva GA,Czeisler C,Niece KL,et al.Selective differentiation of neural progenitor cells by high-epitope density nanofibers. Science.2004;303(5662): 1352-1355.
[12] Zhang S,Greenfield MA,Mata A,et al.A self-assembly pathway to aligned monodomain gels.Nat Mater. 2010; 9(7):594-601.
[13] Ma PX,Zhang R.Synthetic nano-scale fibrous extracellular matrix. J Biomed Mater Res.1999;46(1):60-72.
[14] Yang F,Murugan R,Ramakrishna S,et al.Fabrication of nano-structured porous PLLA scaffold intended for nerve tissue engineering.Biomaterials.2004;25(10): 1891-1900.
[15] Liu X,Ma PX.Phase separation,pore structure, and properties of nanofibrous gelatin scaffolds.Biomaterials. 2009;30(25): 4094-4103.
[16] Greiner A,Wendorff JH.Electrospinning:a fascinating method for the preparation of ultrathin fibers.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007; 46(30): 5670-5703.
[17] Dersch R,Liu T,Schaper AK,et al.Electrospun nanofibers: Internal structure and intrinsic orientation.J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem.2003;41(4):545-553.
[18] Li WJ,Tuli R,Huang X,et al.Multilineage differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in a three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold. Biomaterials.2005;26(25): 5158-5166.
[19] Ohkawa K,Cha D,Kim H,et al.Electrospinning of chitosan. Macromol Rapid Commun.2004;25(18):1600-1605.
[20] Kidoaki S,Kwon IK,Matsuda T.Mesoscopic spatial designs of nano- and microfiber meshes for tissue-engineering matrix and scaffold based on newly devised multilayering and mixing electrospinning techniques.Biomaterials.2005;26(1): 37-46.
[21] Um IC,Fang D,Hsiao BS,et al.Electro-spinning and electro-blowing of hyaluronic acid. Biomacromolecules. 2004; 5(4):1428-1436.
[22] Neal RA,McClugage III SG,Link MC,et al.Laminin nanofiber meshes that mimic morphological properties and bioactivity of basement membranes.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2008; 15(1):11-21.
[23] Mao HQ,Lim SH,Zhang S,et al.The Nanofiber Matrix as an Artificial Stem Cell Niche.Biomaterials as Stem Cell Niche, Studies in Mechanobiology Tissue Engineering and Biomaterials. 2010;2:89-118.
[24] Stevens MM,George JH.Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface. Science.2005;310(5751):1135-1138.
[25] Hackney JA,Charbord P,Brunk BP,et al.A molecular profile of a hematopoietic stem cell niche.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99(20):13061-13066.
[26] Nishikawa M,Tahara T,Hinohara A,et al.Role of the microenvironment of the embryonic aorta-gonad-mesonephros region in hematopoiesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci.2001; 938:109-116.
[27] Bagley J,Rosenzweig M,Marks DF,et al.Extended culture of multipotent hematopoietic progenitors without cytokine.Exp Hematol.1999;27(3):496-504.
[28] Li Y,Ma T,Kniss DA,et al.Human cord cell hematopoiesis in three-dimensional nonwoven fibrous matrices: in vitro simulation of the marrow microenvironment. J Hematother Stem Cell Res.2001;10(3):355-368.
[29] Nur-E-Kamal A,Ahmed I,Kamal J,et al.Three-dimensional nanofibrillar surfaces promote self-renewal in mouse embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells.2006;24(2): 426-433.
[30] Shih YR,Chen CN,Tsai SW,et al.Growth of mesenchymal stem cells on electrospun type I collagen nanofibers.Stem Cells.2006;24(11):2391-2397.
[31] Hosseinkhani H,Hosseinkhani M,Tian F,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in self-assembled peptide-amphiphile nanofibers. Biomaterials. 2006;27(22): 4079-4086.
[32] Carpenter MK,Cui X,Hu ZY,et al.In vitro expansion of a multipotent population of human neural progenitor cells.Exp Neurol.1999;158(2):265-278.
[33] Sen A,Kallos MS,Behie LA.Passaging protocols for mammalian neural stem cells in suspension bioreactors. Biotechnol Prog.2002;18(2):337-345.
[34] Christopherson GT,Song H,Mao HQ.The influence of fiber diameter of electrospun substrates on neural stem cell differentiation and proliferation.Biomaterials. 2009;30(4): 556-564.
[35] Nisbet DR,Yu LM,Zahir T,et al.Characterization of neural stem cells on electrospun poly (-caprolactone) submicron scaffolds: evaluating their potential in neural tissue engineering.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2008;19(5):623-634.
[36] Gimble JM,Katz A J,Bunnell BA.Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine.Circulation research. 2007;100(9): 1249-1260.
[37] Wang M.Developing bioactive composite materials for tissue replacement. Biomaterials.2003;24(13):2133-2151.
[38] Guda T,Appleford M,Oh S,et al.A cellular perspective to bioceramic scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: the state of the art.Curr Top Med Chem.2008;8(4): 290-299.
[39] Schneider OD,Loher S,Brunner TJ,et al.Cotton wool-like nanocomposite biomaterials prepared by electrospinning: in vitro bioactivity and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;84(2):350-362.
[40] Mavis B,Demirtas TT,Gumusderelioglu M,et al.Synthesis, characterization and osteoblastic activity of polycaprolactone nanofibers coated with biomimetic calcium phosphate.Acta Biomater.2009;5(8):3098-3111.
[41] Lee JH,Rim NG,Jung HS,et al.Control of osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of human mesenchymal stem cells on composite nanofibers containing poly[lactic-co-(glycolic acid)] and hydroxyapatite.Macromol Biosci. 2010;10(2):173-182.
[42] Li WJ,Tuli R,Okafor C,et al.A three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering using human mesenchymal stem cells.Biomaterials. 2005;26(6): 599-609.
[43] Lim SH,Liu XY,Song H,et al.The effect of nanofiber-guided cell alignment on the preferential differentiation of neural stem cells. Biomaterials.2010;31(34): 9031-9039.
[44] Cho YI,Choi JS,Jeong SY,et al.Nerve growth factor (NGF)-conjugated electrospun nanostructures with topographical cues for neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6(12): 4725-4733.
[45] Jiang X,Cao HQ,Shi LY,et al.Nanofiber topography and sustained biochemical signaling enhance human mesenchymal stem cell neural commitment.Acta Biomaterialia.2012;8(3):1290-1302.
[46] Xie J,Willerth SM,Li X,et al.The differentiation of embryonic stem cells seeded on electrospun nanofibers into neural lineages.Biomaterials.2009;30(3): 354-362.
[47] Chew SY,Mi R,Hoke A,et al.The effect of the alignment of electrospun fibrous scaffolds on Schwann cell maturation. Biomaterials.2008;29(6):653-661.
[48] Chew SY,Mi R,Hoke A,et al.Aligned Protein-Polymer Composite Fibers Enhance Nerve Regeneration: A Potential Tissue-Engineering Platform.Adv Funct Mater. 2007;17(8): 1288-1296.
[49] Silva GA,Czeisler C,Niece KL,et al.Selective differentiation of neural progenitor cells by high-epitope density nanofibers. Science.2004;303(5662): 1352-1355.
[50] Dang JM,Leong KW.Myogenic induction of aligned mesenchymal stem cell sheets by culture on thermally responsive electrospun nanofibers.Adv Mater. 2007;19(19): 2775-2779.
[51] Choi JS,Lee SJ,Christ GJ,et al.The influence of electrospun aligned poly(epsilon-caprolactone)/collagen nanofiber meshes on the formation of self-aligned skeletal muscle myotubes.Biomaterials.2008;29(19):2899-2906.
[52] Zhao CP,Zhang C,Zhou SN,et al.Human mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate the phenotype of SOD1-G93A ALS mice.Cytotherapy.2007;9(5):414-426.
[53] Parr AM,Kulbatski I,Zahir T,et al.Transplanted adult spinal cord-derived neural stem/progenitor cells promote early functional recovery after rat spinal cord injury. Neuroscience. 2008;155(3):760-770.
[54] Daadi MM,Maag AL,Steinberg GK.Adherent self-renewable human embryonic stem cell-derived neural stem cell line: functional engraftment in experimental stroke model.PLoS One.2008;3(2):e1644.
[55] Mooney DJ,Vandenburgh H.Cell delivery mechanisms for tissue repair. Cell Stem Cell.2008;2(3):205-213.
[56] Li WJ,Chiang H,Kuo TF,et al.Evaluation of articular cartilage repair using biodegradable nanofibrous scaffolds in a swine model: a pilot study.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2009;3(1):1-10.
[57] Hashi CK,Zhu Y,Yang GY,et al.Antithrombogenic property of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in nanofibrous vascular grafts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(29): 11915-11920.
[58] Davis ME,Motion JP,Narmoneva DA,et al.Injectable self-assembling peptide nanofibers create intramyocardial microenvironments for endothelial cells. Circulation. 2005; 111(4):442-450. |
| [1] | He Xue-feng, Xiong Ai-bing. Application and research progress of three-dimensional printing in the field of orthopaedics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 428-432. |
| [2] | He Yan-ping, Ma De-chun, Li Lei, Zhang Li, Zheng Shuang, Dong Ke-xin. Hemocompatibility and surface modification of artificial blood vessel materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1272-1276. |
| [3] | Tan Wei, Lv Hai, Zhou Chu-song. Acellular matrix scaffold for tissue-engineered intervertebral disc which is closest to the normal three-dimensional structure of the nucleus pulposus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1289-1294. |
| [4] | Wu Yan, Huang Lan . Bone morphogenetic protein 9-induced osteogenic differentiation of dental follicle cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2255-2260. |
| [5] |
Du Wei-bin, Quan Ren-fu, Zheng Xuan, Wang Tuo.
Hair follicle stem cells promote the healing of skin wound
|
| [6] | Huang Zhe. Correlation between Bmi-1 and clinicopathological features of colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 894-899. |
| [7] | Zhang Bao-hua, Qiu Fu-cheng, Dong Ci1, Han Rui, Zhang Yong-zhi, Liu Hui-miao,Xie Bing-chuan, Zhang Li-na, Wang Wen-ting, Wang Yan-yong, Zhang Zhen-qing, Gu Ping,Yan Bao-yong. Neural stem cell transplantation for central nervous system diseases via the cerebrospinal fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(6): 974-978. |
| [8] | Li Bing-ting, Jia Ying-zhen, Liu Zhi-fang, Song Yuan, Hou Xiao-wei. Effect of freeze-dried bone xenograft and platelet-rich fibrin compound on osteogenesis and osseointegration of alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8376-8381. |
| [9] | Wang Xiao-dong, Zhang Yong-hong. Preparation and performance of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2-poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyoctanoate) nanospheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8405-8408. |
| [10] | Feng Chao, Li Zhe, Lv Xiang-guo, Xu Yue-min, Fu Qiang. In vitro preparation and biochemical evaluation of oxygen generative keratin/silk fibroin compound biomaterial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8480-8486. |
| [11] | Wang Teng-bin, Zhu Hui, Li Tian-shi . Development of chitosan and its derivative scaffolds for tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8498-8503. |
| [12] | Li Tian-shi, Zeng Wen-ni, He Jun-jun. Chitin and its derivatives inhibit scar formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(52): 8504-8508. |
| [13] | Ma Song-feng, Cao Hui, Zheng Feng, Qiao Jun, Zhang Guo-ming. Concomitant cardiac valve replacement and coronary artery bypass grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 699-704. |
| [14] | Liu Yang, Li Xiao-yan, Chen Pan-pan, Li Jun . Bone marrow stem cell transplantation for improving heart function of patients with acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6689-6695. |
| [15] | Lu Hua-ding, Lian Li-yi, Chen Ming-wei, Dai Yu-hu. Cloning and expression of Asperguillus endo-chitosanase gene in Escherichia coli [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5490-5496. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||